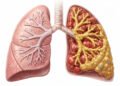
The Best Ways to Stop Smoking: Understanding the Dangers of Smoking and Effective Quitting Strategies
Key Takeaways
- Smoking damages virtually every organ system and remains the leading cause of preventable death.
- Nicotine addiction combines powerful physiological dependence with deeply ingrained behavioural patterns.
- Evidence-based methods include nicotine replacement therapy, prescription medications, and behavioural support.
- A personalised quit plan and professional guidance significantly improve success rates.
Table of Contents
Introduction: Breaking Free from Tobacco’s Deadly Grip
Smoking remains one of the most devastating health crises of our time, claiming over seven million lives annually and standing as the leading cause of preventable disease and death worldwide. Despite widespread awareness of its dangers, millions continue to struggle with tobacco addiction, trapped in a cycle that damages virtually every organ system in the human body. The journey toward freedom from smoking begins with understanding both the profound health consequences of continued tobacco use and the comprehensive arsenal of best smoking cessation methods available to those ready to quit.
The path to becoming smoke-free is rarely straightforward, as nicotine addiction creates powerful physiological dependencies while smoking behaviors become deeply embedded in daily routines, emotional responses, and social interactions. However, modern medicine and behavioral science have developed increasingly effective strategies to help smokers successfully break free from tobacco dependence. This comprehensive guide will explore the immediate and long-term dangers of smoking, examine why quitting proves so challenging for most people, and detail the most effective evidence-based cessation methods available today.
Throughout this exploration, we’ll provide a detailed analysis of nicotine replacement therapy options, compare the relative risks of vaping versus traditional smoking, and offer practical guidance for implementing successful quit strategies. Whether you’re a healthcare professional supporting patients through cessation efforts or an individual contemplating your own quit journey, understanding these proven methodologies can make the difference between another failed attempt and lasting freedom from tobacco addiction.
Dangers of Smoking Explained: The Devastating Health Consequences
The dangers of smoking explained extend far beyond the commonly understood risk of lung cancer, encompassing a catastrophic cascade of health effects that begin within minutes of lighting a cigarette and compound over years of continued use. When tobacco smoke enters the body, it immediately triggers acute physiological responses, including elevated heart rate, increased blood pressure, and reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. These immediate effects strain the cardiovascular system and create conditions that, with repeated exposure, lead to permanent damage throughout the body.
The long-term consequences of smoking represent one of medicine’s most extensively documented health disasters, with tobacco use directly linked to numerous life-threatening conditions. Lung cancer remains the most notorious smoking-related disease, with tobacco use responsible for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases. However, smoking harms extend throughout the respiratory system, causing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and chronic bronchitis that progressively destroy lung function and leave individuals struggling to breathe.
Cardiovascular disease represents another major category of smoking-related health problems, with tobacco use dramatically increasing risks of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. The chemicals in cigarette smoke damage blood vessel walls, promote the formation of dangerous blood clots, and accelerate the development of atherosclerosis. Smokers face twice the risk of coronary heart disease compared to non-smokers, while their stroke risk increases by 2–4 times. These cardiovascular effects contribute significantly to the reduced life expectancy observed among smokers, who, on average, die 10 years earlier than their non-smoking counterparts.
Beyond respiratory and cardiovascular systems, smoking causes cancer throughout the body, including bladder, cervical, colorectal, oesophageal, kidney, pancreatic, and stomach cancers. The carcinogenic compounds in tobacco smoke circulate throughout the bloodstream, causing DNA damage in cells far from the respiratory tract. Additionally, smoking compromises immune system function, delays wound healing, reduces bone density, and contributes to reproductive health problems, including infertility and pregnancy complications. The comprehensive nature of smoking harms underscores why cessation represents one of the most essential health interventions available to current smokers.
Want to quit smoking? Scientists say these 3 methods work best.
Understanding the health impacts of addiction can lead to better treatment.
Why Quitting Smoking is Hard: Understanding the Complex Challenge
Understanding why quitting smoking is hard requires examining the multifaceted nature of tobacco addiction, which combines powerful physiological dependence with deeply ingrained behavioural patterns and psychological associations. At the core of this difficulty lies nicotine addiction, a complex neurochemical process that fundamentally alters brain function and creates compelling urges to continue smoking. When nicotine reaches the brain, it binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It triggers the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters in the brain’s reward pathways, creating pleasurable sensations that reinforce continued use.
The physiological aspects of nicotine dependence become apparent when smokers attempt to quit, leading to withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, concentration difficulties, and intense cravings. These symptoms often peak within the first few days of quitting and can last several weeks, making sustained abstinence a significant challenge without proper support and coping strategies.
Learn about how addiction therapy can aid in recovery.
Discover relapse prevention strategies to enhance your recovery journey.
Explore natural remedies for anxiety that might help during withdrawal.
Effective Cessation Methods
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): Patches, gum, lozenges, inhalers, and nasal sprays provide controlled doses of nicotine to ease withdrawal.
- Prescription Medications: Varenicline and bupropion reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms by targeting neural pathways.
- Behavioural Support: Counselling, support groups, and quitlines help modify smoking behaviours and develop coping skills.
- Digital Tools: Mobile apps and online programs offer personalised quit plans, progress tracking, and motivational messaging.
- Vaping vs. Smoking: While e-cigarettes eliminate combustion, they still deliver nicotine and require cautious consideration as a harm-reduction tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How long does nicotine withdrawal last?
Withdrawal symptoms typically peak within 2–3 days after quitting and subside significantly after 2–4 weeks. However, psychological cravings may persist for months.
-
Is vaping a safe way to quit smoking?
Vaping may be less harmful than traditional smoking due to the absence of combustion, but it still exposes users to nicotine and potentially harmful chemicals. Consult a healthcare professional before using e-cigarettes as a quit aid.
-
What is the most effective quit strategy?
Combining pharmacotherapy (NRT or prescription medications) with behavioural support yields the highest success rates. Tailoring the plan to your needs and seeking professional guidance maximises your chances of quitting for good.
-
Can cold turkey quitting work?
Some smokers succeed with a cold turkey approach, but relapse rates are higher compared to structured methods. Incorporating support and coping strategies improves outcomes.
-
Where can I find additional support?
Reach out to local quit-lines, healthcare providers, support groups, and Meducate Courses for personalised guidance and encouragement throughout your quit journey.