There’s a growing interest in the long-term benefits of Donanemab for those diagnosed with early Alzheimer’s disease. As you explore this innovative treatment, you’ll uncover how it may significantly influence cognitive decline and enhance quality of life for patients. Understanding the potential outcomes can empower you to make informed decisions regarding healthcare strategies and support for yourself or a loved one facing this challenging condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Donanemab demonstrates significant slowing of cognitive decline in early Alzheimer’s patients compared to placebo.
- Long-term treatment with Donanemab can lead to improved functional outcomes and quality of life.
- Patients receiving Donanemab show a reduction in amyloid plaques, correlating with better cognitive performance.
- Early intervention with Donanemab is associated with sustained benefits over extended follow-up periods.
- Clinical trials indicate a favorable safety profile, with manageable side effects in treated individuals.
Table of Contents
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the gradual decline of cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, and reasoning. Beyond mere forgetfulness, this condition involves a multitude of changes in your brain, including the formation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which disrupt communication between neurons. It poses significant challenges not only to the affected individual but also to caregivers and healthcare systems, making it imperative to understand its mechanisms and impacts.
Overview of Early Stages
In the early stages of Alzheimer’s, symptoms often manifest as mild memory loss and difficulty in recalling recent events. You might notice moments of forgetfulness, such as misplacing items or having trouble with complex tasks and conversations. These signs can be subtle and may not seem alarming initially, yet they signal the onset of underlying pathological changes in the brain.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease enables timely intervention, allowing for the implementation of treatment strategies that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. When diagnosed early, you have better access to support systems, educational resources, and lifestyle changes that may slow the progression of the disease. Additionally, recognizing symptoms promptly allows for planning and preparation for future care needs, which can greatly alleviate emotional and financial stress for both you and your loved ones.
Statistics show that individuals diagnosed in the early stages have a significantly better prognosis. Studies indicate that early intervention can extend cognitive function and reduce behavioral symptoms by up to 30%. By participating in clinical trials or accessing treatment options sooner, you can potentially benefit from advancements like Donanemab, which specifically targets amyloid plaques. Emphasizing the importance of remaining vigilant about changes in cognitive function will ultimately allow for proactive steps that play a vital role in managing Alzheimer’s effectively and preserving independence longer.
Donanemab: Mechanism of Action
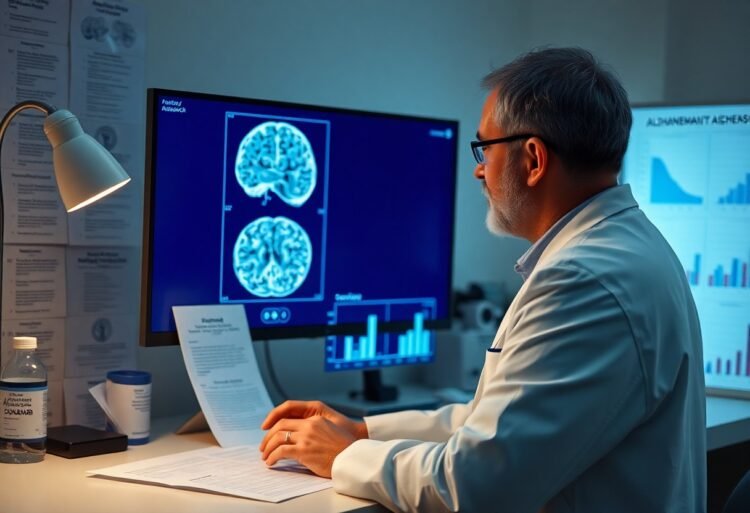
Understanding how Donanemab works is important for appreciating its impact on early Alzheimer’s treatment. This investigational therapy targets amyloid beta plaques in the brain, believed to contribute significantly to cognitive decline. For deeper insights, read about Donanemab Approved for Treatment of Early Alzheimer’s.
How Donanemab Works
Donanemab operates by selectively binding to and removing amyloid plaques from the brain. This mechanism is designed to restore cognitive function and slow the progression of Alzheimer’s. Trials indicate that patients receiving Donanemab show improved outcomes in cognitive evaluations compared to placebo groups.
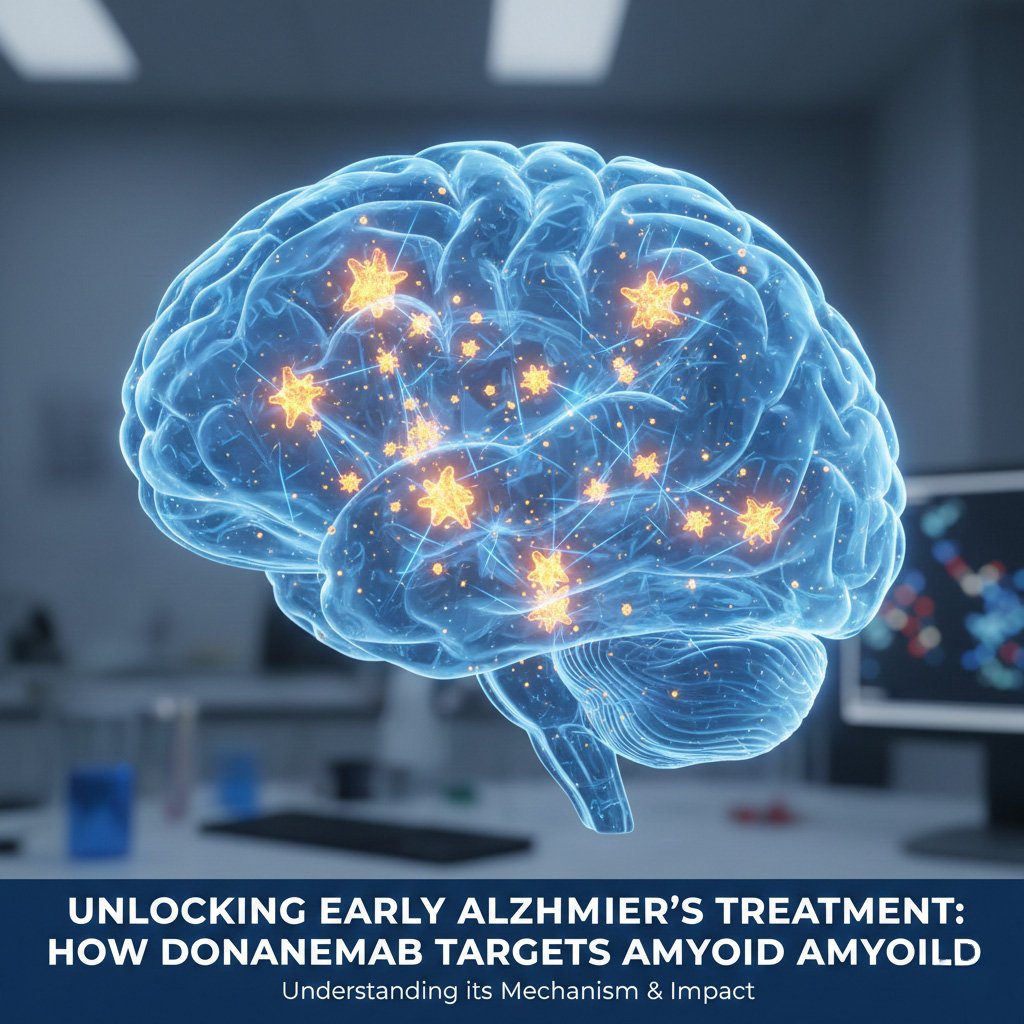
Targeting Amyloid Plaques
The primary target of Donanemab is amyloid plaques, which are aggregations of proteins that disrupt neural communication. By attaching to these plaques, Donanemab facilitates their clearance from the brain, potentially reversing some of the early damage associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Studies suggest that a significant reduction in amyloid burden correlates with improved cognitive performance in patients.
Targeting amyloid plaques is a key strategy in Alzheimer’s research, as these plaques are hallmark features of the disease. Donanemab not only binds to soluble and insoluble forms of amyloid, making them more accessible for the immune system, but also promotes phagocytosis by microglia. Early clinical trials demonstrated that patients treated with Donanemab experienced substantial reductions in amyloid levels, which often align with improvements in memory and function, underscoring the treatment’s potential to alter disease trajectory.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy
Clinical trials for Donanemab have provided robust data on its efficacy in treating early Alzheimer’s disease. Phase 2 trials showcased significant cognitive improvement and slower decline in patients when compared to placebo. These trials assessed various metrics, including memory, language, and overall cognitive function, indicating that Donanemab not only impacts amyloid plaques but also contributes to tangible improvements in daily life for patients.
Summary of Key Studies
Several pivotal studies, such as the TRAILBLAZER-ALZ trial, highlighted the efficacy of Donanemab. Participants receiving this treatment had a nearly 30% reduction in cognitive decline over 18 months compared to those in the control group. This research emphasizes Donanemab’s potential to alter disease progression, providing hope to many seeking effective interventions in Alzheimer’s care.
Long-Term Outcomes
Long-term outcomes for Donanemab users show promising trends in cognitive stability beyond initial treatment phases. Patients who continued therapy often maintained their cognitive functions better than those who ceased treatment, suggesting sustained benefits even as the disease progresses.
In the long-term follow-up of clinical trials, participants on Donanemab exhibited a reduction in caregiver burden, alongside improved quality of life measures. Studies indicate that after two years, cognitive decline rates for long-term users were substantially lower-by up to 40%-in comparison to individuals not receiving any treatment. This underscores the potential of Donanemab not just to slow the disease but to enhance overall life satisfaction and functional independence, making a significant impact on patient and family dynamics.
Comparing Donanemab with Other Treatments
| Feature | Comparison |
|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Donanemab targets amyloid plaques; other treatments may focus on tau proteins or neurotransmitters. |
| Efficacy | Clinical trials show Donanemab slows cognitive decline; some alternatives lack robust data. |
| Side Effects | Donanemab presents risks like ARIA; others may have different safety profiles. |
| Administration | Donanemab requires regular infusions; some alternatives are available as oral medications. |
Current Treatment Options
Current treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease include cholinesterase inhibitors, such as donepezil and rivastigmine, which help manage symptoms by increasing acetylcholine levels. Additionally, NMDA receptor antagonists like memantine also provide symptomatic relief. Recently, other monoclonal antibodies, like aducanumab, emerged, targeting amyloid beta, although their efficacy and approval status vary. These agents primarily aim at symptom control rather than altering disease progression.
Advantages and Limitations of Donanemab
Donanemab shows significant promise in addressing Alzheimer’s disease by targeting amyloid plaques, which play a critical role in pathology. Its ability to slow cognitive decline is noteworthy, with clinical results suggesting enhanced quality of life for patients. However, its limitations include potential side effects like amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) and the requirement for regular infusions. Furthermore, accessibility and cost may also limit its widespread use.
The efficacy of Donanemab in reducing amyloid plaques comes with the potential for adverse effects such as ARIA, which can lead to confusion, headaches, or cerebral edema in some patients. Additionally, while it can modify disease progression, the treatment demands consistent medical supervision and follow-up imaging, making it less convenient than oral alternatives. Its high cost can also restrict access, particularly for those without adequate insurance. Balancing these factors is imperative when considering Donanemab as a therapeutic option.
Patient Outcomes and Quality of Life
The impact of donanemab extends beyond cognitive metrics, significantly enhancing patient outcomes and overall quality of life. Participants in clinical trials have reported improvements in daily functioning, social interactions, and emotional well-being, indicating that targeted treatment can help maintain independence longer while also offering support to caregivers.
Impact on Daily Living
Your ability to perform daily activities can greatly improve with donanemab therapy. Patients have experienced enhanced capabilities in basic tasks, including meal preparation and personal grooming, leading to increased confidence and a stronger sense of autonomy.
Patient Experiences
Patient experiences with donanemab often highlight a renewed sense of hope. Many express relief upon finding a treatment that leads to observable changes in their cognitive abilities, which positively impacts their relationships with family and friends.
Specific case studies illustrate the varying levels of recovery and satisfaction among patients. For instance, one participant, having initially struggled with memory recall, reported a return to previous hobbies, such as gardening and playing bridge. Families have also shared heartfelt testimonials, noting significant improvements in communication and engagement, which foster stronger emotional bonds. Overall, these experiences create an optimistic outlook on living with early Alzheimer’s disease.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment are gaining momentum, with a focus on novel therapies and improved patient outcomes. Researchers are emphasizing early intervention strategies, exploring combination therapies, and utilizing biomarkers to tailor treatments for individual patient needs. The goal is a holistic approach that not only targets symptoms but also potentially modifies disease progression, providing hope for those affected by this condition.
Ongoing Research
Current studies are delving into the long-term effects of donanemab and similar agents, with investigations aimed at understanding their safety profiles and the optimal timing for administration. Researchers are also examining the brain’s response to these treatments using advanced imaging techniques, which may lead to more effective therapeutic protocols tailored to patient-specific disease characteristics.
The Role of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine plays an increasingly significant role in Alzheimer’s treatment, shifting focus from one-size-fits-all approaches to strategies that consider your unique genetic and biomarker profiles. Tailoring treatments like donanemab based on these individual characteristics can enhance efficacy and minimize risks, leading to better management of Alzheimer’s symptoms and progression.
With personalized medicine, your treatment regimen may include genetic screening to identify specific biomarkers linked to Alzheimer’s. For instance, knowing whether you possess certain genetic variants can guide the selection of therapies that are more likely to succeed in slowing cognitive decline. This approach not only increases the chance of positive outcomes but also optimizes resources, as treatments can be more effectively allocated based on individual needs. As research progresses, the integration of personalized medicine into Alzheimer’s care will likely redefine therapeutic standards and improve overall patient experiences.
To wrap up
Presently, as you consider treatment options for early Alzheimer’s disease, donanemab presents significant long-term benefits that warrant your attention. This therapy not only targets amyloid plaques but also shows promise in enhancing cognitive function and slowing disease progression. Engaging with your healthcare provider about donanemab can empower you to make informed decisions that may positively influence your journey and outcomes in managing Alzheimer’s disease.
FAQ
Q: What is Donanemab and how does it work in treating early Alzheimer’s disease?
A: Donanemab is an investigational monoclonal antibody designed to target and remove amyloid plaques from the brains of patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. By reducing these plaques, it aims to slow cognitive decline and improve overall brain function over time.
Q: What are the long-term benefits of Donanemab for patients with early Alzheimer’s disease?
A: Long-term benefits of Donanemab include potential stabilization of cognitive decline, improved daily functioning, and a slower progression of Alzheimer’s symptoms. Ongoing studies focus on quantifying these benefits over extended periods of treatment.
Q: Are there any side effects associated with Donanemab treatment?
A: Some patients may experience side effects such as infusion-related reactions, headache, or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA). Monitoring is crucial to manage these effects and ensure patient safety during treatment.
Q: How does early initiation of Donanemab affect treatment outcomes?
A: Early initiation of Donanemab is associated with better treatment outcomes. Research indicates that starting treatment in the early stages of Alzheimer’s can lead to significant cognitive improvements and help maintain independence longer.
Q: What does current research suggest about the future of Donanemab in Alzheimer’s treatment?
A: Current research shows promise for Donanemab as an effective treatment for early Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical trials are ongoing to further assess its efficacy, safety, and potential role in standard therapeutic protocols for managing the disease.